Housing Market Cycles refer to the recurring patterns of expansion and contraction in the housing sector over time. These cycles play a major role in shaping home prices, construction activity, buyer behavior, and overall economic stability. Understanding Real Estate Market Cycles helps homeowners, investors, and policymakers make informed decisions and reduce risks associated with sudden market changes.
Understanding Real Estate Market Cycles
Real Estate Market Cycles generally move through four main stages: recovery, expansion, peak, and contraction. Each phase reflects changes in supply, demand, interest rates, and economic conditions.
Phases of Housing Market Cycles
| Phase | Characteristics |
| Recovery | Low prices, slow sales, improving economic conditions |
| Expansion | Rising demand, increasing prices, new construction |
| Peak | High prices, strong demand, market saturation |
| Contraction | Falling prices, reduced demand, higher foreclosures |
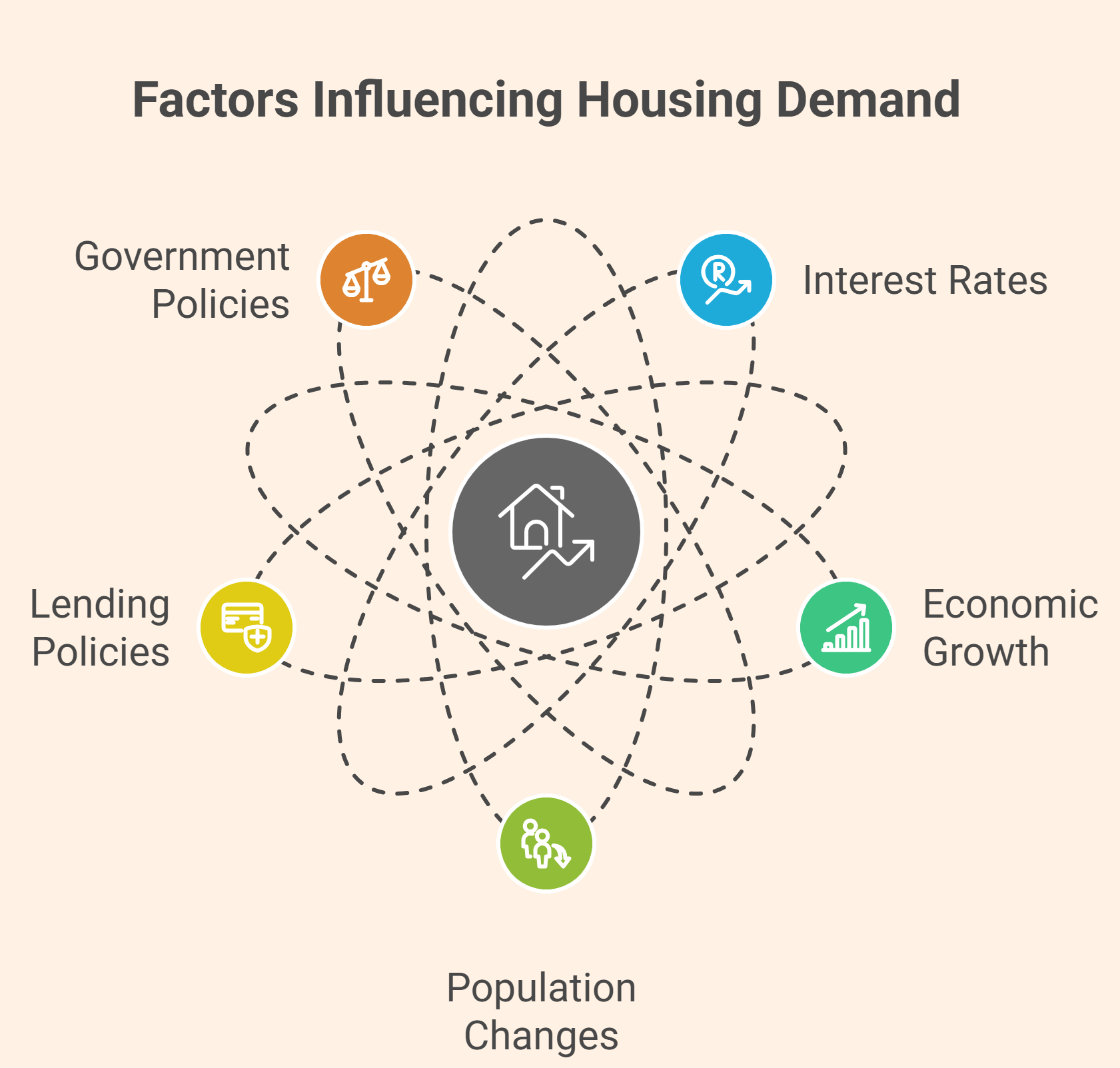
Causes of Housing Market Cycles
The Causes of Housing Market Cycles are influenced by both economic and social factors. These forces interact to create periods of growth and decline.
Key Causes| Cause | Explanation |
| Interest Rates | Lower rates increase borrowing; higher rates reduce demand |
| Economic Growth | Strong job markets boost home buying |
| Population Changes | Migration and population growth affect housing demand |
| Lending Policies | Easy credit can inflate housing bubbles |
| Government Policies | Taxes, subsidies, and regulations shape market behavior |
These factors contribute to Boom and Bust Cycles in Housing, where rapid growth is often followed by sharp downturns.
Housing Market Fluctuations
Housing Market Fluctuations occur when prices and demand change due to economic uncertainty, inflation, or shifts in consumer confidence. Sudden fluctuations can create instability, especially for first-time buyers and renters.
Common Signs of Market Fluctuations
- Rapid price increases or declines
- Changes in housing inventory
- Rising mortgage default rates
- Decreased construction activity
Effects of Housing Market Cycles
The Effects of Housing Market Cycles impact individuals, businesses, and the broader economy.
Major Effects
Group Affected | Impact |
Homeowners | Changes in home equity and affordability |
Investors | Profit opportunities or financial losses |
Construction Industry | Job growth or layoffs |
Economy | Influence on employment and financial stability |
Severe downturns during Boom and Bust Cycles in Housing can lead to economic recessions, while strong expansions may increase wealth but reduce affordability.
Importance of Understanding Housing Market Cycles
Understanding Housing Market Cycles helps people make smarter long-term decisions. Buyers can avoid purchasing at market peaks, while policymakers can introduce regulations to limit extreme market volatility.
Conclusion
Housing Market Cycles are a fundamental part of the real estate industry. Influenced by economic conditions, interest rates, and policy decisions, these cycles drive Housing Market Fluctuations and shape the Real Estate Market Cycles we experience over time. By understanding the Causes of Housing Market Cycles and recognizing their Effects, individuals and governments can better prepare for future market changes and reduce financial risk.
Read More: Understanding Stamp Duty
Read More: Property Transfer in India
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What are Housing Market Cycles?
Ans. Housing Market Cycles are repeating phases of growth and decline in housing prices and demand.
Q2: What causes Boom and Bust Cycles in Housing?
Ans. They are caused by rapid economic growth, easy credit, rising demand, followed by market saturation and economic slowdowns.
Q3: How do Housing Market Fluctuations affect buyers?
Ans. Fluctuations can change affordability, mortgage rates, and the availability of homes.
Q4: Why is understanding Real Estate Market Cycles important?
Ans. It helps buyers, investors, and policymakers reduce risks and make informed decisions.





Join The Discussion