Stamp Duty is an essential financial and legal charge in India that is applicable to legal agreements, property transactions and financial instruments. Understanding the Stamp Duty in India can help buyers investors, sellers, and buyers save money and assures legal ownership transfer. This guide will explain everything you should be aware of about Stamp Duty rates, their rate as well as calculation methods and state-specific variations.
What is Stamp Duty?
Stamp Duty tax is imposed from the State Government on documents that document transactions. In India the country, it is administered by the Indian Stamp Act, 1899 as well as the respective State Stamp Acts.
The payment of Stamp Duty makes documents legally valid and admissible to courts. In the absence of Stamp duty payment, papers such as lease agreements, sale deeds or gift deeds will have no legal validity.
Why is Stamp Duty Important?
- Establishes legal ownership
- Prevents property fraud
- Mandatory for property registration
- Ensures compliance with Indian property laws
- Required for loan approvals and legal disputes
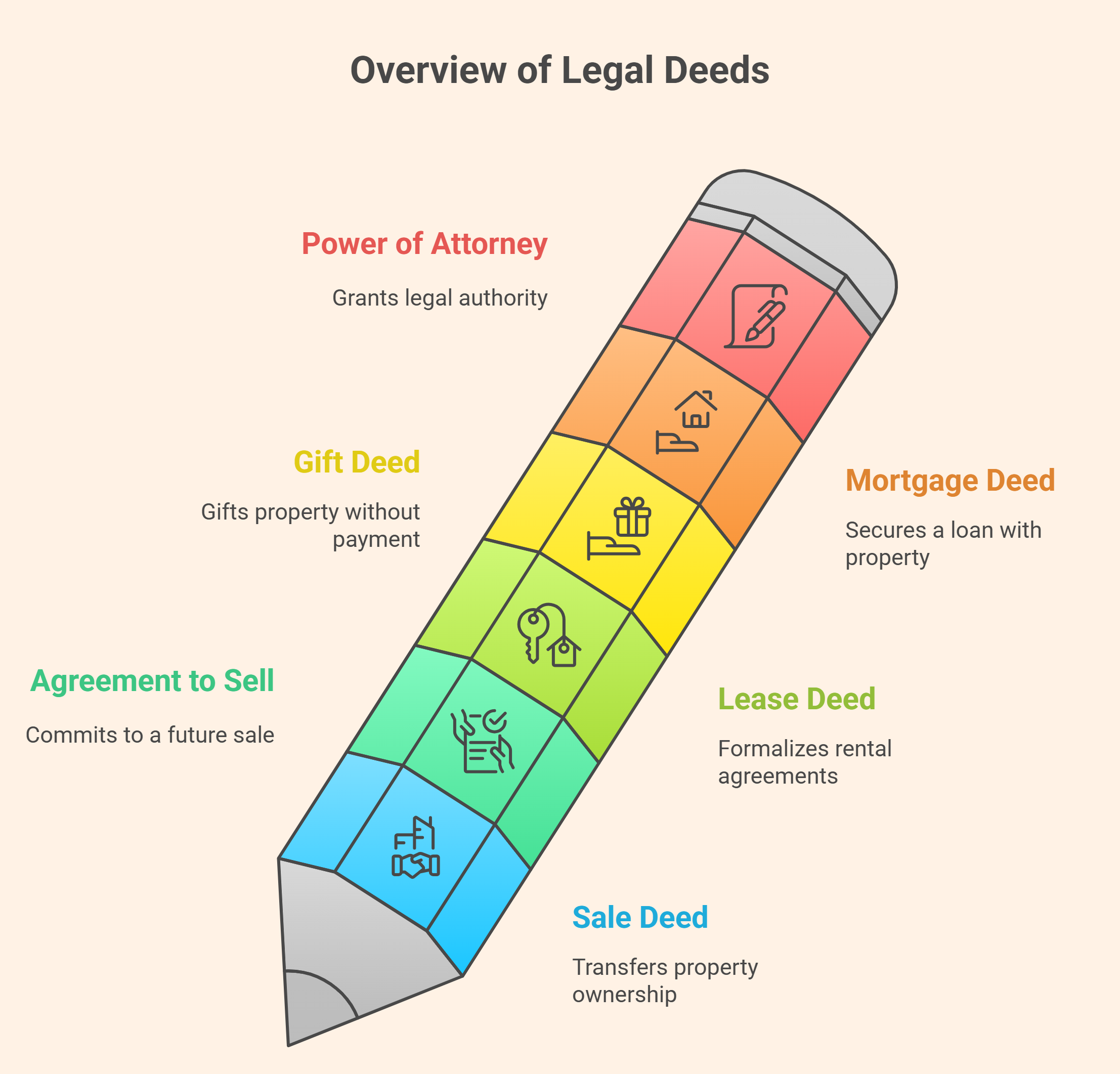
Documents That Require Stamp Duty in India
| Document Type | Purpose |
| Sale Deed | Property ownership transfer |
| Agreement to Sell | Future sale commitment |
| Lease Deed | Rental or lease agreement |
| Gift Deed | Property gifted without payment |
| Mortgage Deed | Loan security |
| Power of Attorney | Legal authority transfer |
Stamp Duty Rates in India (State-Wise Overview)
Stamp Duty rates vary from state to state and are generally calculated as a percentage of the circle rate or market value, whichever is higher.
State | Stamp Duty Rate |
Maharashtra | 5% |
Delhi | 4%–6% |
Karnataka | 5% |
Tamil Nadu | 7% |
Uttar Pradesh | 7% |
Rajasthan | 6% |
West Bengal | 6%–7% |
Note: Some states offer Stamp Duty concessions for women buyers and first-time homebuyers.
How is Stamp Duty Calculated?
Stamp Duty calculation depends on:
- Property value
- Location
- Property type
- Buyer category
Example:
If the market value of a property in Maharashtra is ₹50 lakh:
- Stamp Duty @ 5% = ₹2.5 lakh
Additional registration charges (usually 1%) may apply separately.
Stamp Duty Payment Methods in India
You can pay Stamp Duty through:
- E-Stamping
- Stamp Paper
- Franking
- Online payment portals
E-Stamping is the most secure and widely used method today, available via authorised banks and government portals.
Difference Between Stamp Duty and Registration Charges
Aspect | Stamp Duty | Registration Charges |
Purpose | Legal validation | Official record |
Payable To | State Government | Sub-Registrar |
Rate | 4%–8% | 1% approx |
Mandatory | Yes | Yes |
Both must be paid to complete property registration in India.
Tax Benefits on Stamp Duty
Under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act, individuals can claim deductions up to ₹1.5 lakh on Stamp Duty paid, subject to conditions:
- Property must be self-occupied
- Claim allowed only in the year of payment
Penalties for Non-Payment of Stamp Duty
- Heavy monetary penalties
- Legal disputes
- Document rejection in court
- Property registration cancellation
Late payment may attract penalties up to 10 times the original Stamp Duty amount, depending on the state.
Recent Updates on Stamp Duty in India
- Some states have implemented temporary Stamp Duty reductions to boost the value of real property
- More widespread adoption of electronic Stamp Duty payment
- Digital property registration systems for enhanced digital properties
Always check the latest Stamp Duty rules of your state before property transactions.
Conclusion
Knowing Stamp Duty in India is crucial for legal property ownership as well as financial planning. Because Stamp Tax rates, the exemptions and payment procedures vary between states, being informed helps ensure compliance and avoids costly penalties. Always check with local authorities or a lawyer prior to finalizing any transaction that involves Stamp Duty.
Read More: Property Transfer in India
Read More: Property Registration Process in India
FAQs on Stamp Duty
Q1. Is Stamp Duty mandatory in India?
Yes, Stamp Duty is mandatory for all legally enforceable documents.
Q2. Who pays Stamp Duty – buyer or seller?
Usually, the buyer pays Stamp Duty in property transactions.
Q3. Can Stamp Duty be refunded?
Refunds are allowed in limited cases if the transaction is cancelled.
Q4. Is Stamp Duty the same across India?
No, Stamp Duty rates vary by state.





Join The Discussion